shell的环境配置文件
根据取得shell的流程不同而读取的环境配置文件不同分为登陆shell(login)和非登陆shell(non-login)。
登陆shell
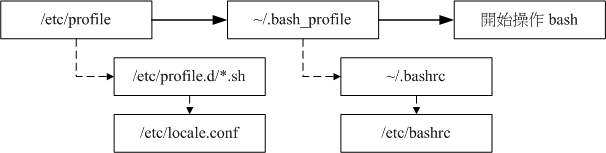
/etc/profile是全局登陆shell配置
~/.bash_profile,~/.bash_login和~/.profile,按顺序优先级根据其存在与否仅读取一个(不同系统不一样,比如:RedHat中只有~/.bash_profile,Debian下只有~/.profile文件)。他们都会读取~/.bashrc,~/.bashrc会读取全局非登陆配置,比如RedHat中是/etc/bashrc,Debian中是/etc/bash.bashrc
非登录shell
仅读取~/.bashrc
基础知识
查看系统支持的shell
1 | |
查看当前用户的shell
1 | |
修改shell,如下命令修改当前用户的shell位bash
1 | |
shell程序
abc.sh
1 | |
参数
$1代表第一个参数,$2代表第二个参数,以此类推。
$0代表文件名
变量
通过variable_name=variable_value定义变量,例如:
1 | |
通过$variable_name或${variable_name}引用变量,例如:
1 | |
只读变量
1 | |
删除变量
1 | |
不能用于只读变量
变量类型
字符串和数值
函数
定义函数
1 | |
调用函数
funname arg1 arg2…
返回值
通过return定义返回值,数值0~255,一般0表示成功,其他为失败。可以通过$?接收返回值
如果没有return语句,则返回值为最后一条语句的运行结果。
当0~255不能满足需求时,也可以通过echo来设定返回值(最后一条语句),使用${函数调用}接收返回值
命令执行结果赋值给变量
1 | |
控制结构
1 | |
&&、||和;
shell执行方式
log-package.sh
1 | |
log-delete.sh
1 | |
shell文件的绝对路径
1 | |
1 | |